Dopamine Biology Diagrams Basic dopamine anatomy. The dopaminergic innervation of the forebrain of mammals is constituted by a small number of highly collateralized neurons (~15,000 - 20,000 on each side of the rat brain) residing in the ventral mesencephalon (Fallon and Loughlin, 1995; Lindvall et al, 1984; Williams and Goldman-Rakic, 1998). Three major divisions of dopaminergic pathways innervate the forebrain and
D1-like dopamine receptor expression and its functions. The D1-like receptor family consists of 2 types of GPCRs that include the D1 and D5 receptors, with a higher density in the striatum or caudo-putamen, nucleus accumbens (NAcc), SN pars reticulata (SNr), and olfactory bulb (OB). 31,32 A moderate expression of D1 receptors has been reported in the entopeduncular nucleus, cerebral aqueduct

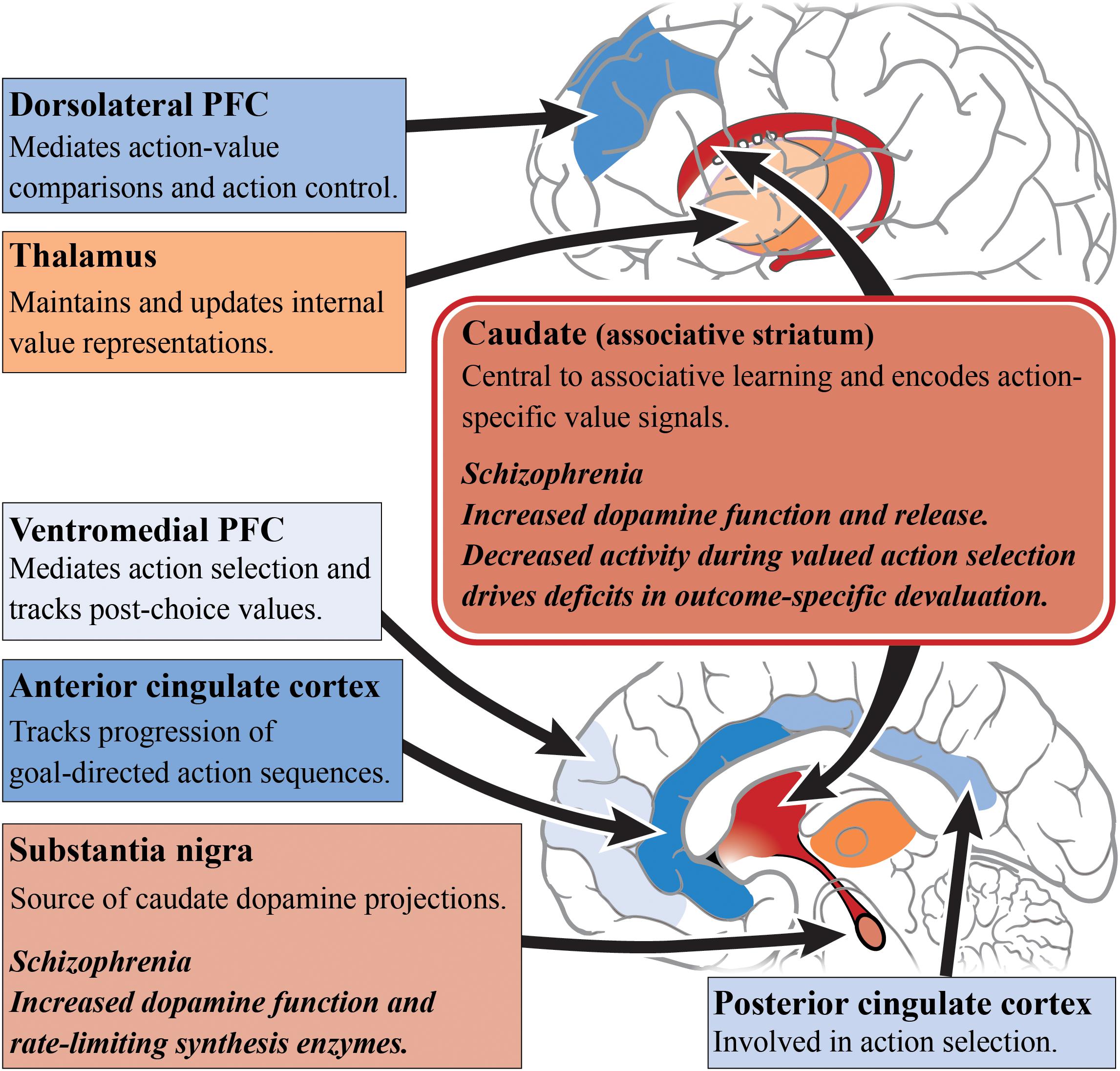
Dopaminergic Systems in the Brain and Pituitary Biology Diagrams
Dopamine (dopaminergic) system plays an important role in central neural system, taking part in regulating motor control, executive functions, motivation, reinforcement, reward, sleep, feeding, attention, cognitive functions, olfaction, vision, hormonal regulation, and outside of central neural system in sympathetic regulation and penile erection. It is now 20 years since Swedish scientists described the existence of the nigrostriatal, mesolimbic, and tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the rat brain [4, 8, 13, 17, 24, 50]. Since then new types of DA neuronal systems in the brain have been mapped

Fig. 1. (A) Cartoon representation of a sagittal section through the human brain showing the major projections of dopamine neurons from the cell bodies in the ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra (VTA/SN) to terminal field areas in the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), nucleus accumbens (N. acc.), and dorsal striatum.(B) Cartoon representation of a typical dopaminergic synapse in the brain. The dopaminergic system plays important roles in neuromodulation, such as motor control, motivation, reward, cognitive function, maternal, and reproductive behaviors. Department of Anatomy, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of Insulin, IGF-1, and muscarinic agonists modulate schizophrenia-associated genes in human The great majority of dopaminergic neurons in the brain (in human 300,000-400,000 cells) is organized in three nuclei, the substantia nigra pars compacta, the ventral tegmental area and the arcuate nucleus. The tuberoinfundibular intermediate-length dopaminergic system controls prolactin release from the anterior pituitary and its

Dopamine: Functions, Signaling, and Association with Neurological ... Biology Diagrams
Midbrain dopaminergic (DA) neurons are located in three major nuclei, including the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc; A9 group), the ventral tegmental area (VTA; A10 group), and the retrorubral field (A8 group) (Figure 1A).DA neurons in SNpc project to dorsal striatum via the nigrostriatal pathway, and regulate voluntary movement control as part of the basal ganglia circuitry. In the present paper the organization of central nervous system dopaminergic pathways is concisely reviewed. Six dopaminergic systems are described: the midbrain efferent system, the tubero-infundibular, the diencephalo-spinal, the incerto-hypothalamic, the periventricular, and the retinal systems. …
