Unattached or incorrectly attached chromosomes promote formation of the Biology Diagrams The spindle checkpoint is an evolutionarily conserved mitotic regulatory mechanism that ensures that anaphase is not attempted until chromosomes are properly aligned on the spindle. Two different cell-cycle transitions must be inhibited by the spindle checkpoint to arrest cells at metaphase and prevent mitotic exit. The checkpoint proteins interact in ways that are more complex than was Bernard, P., Hardwick, K. & Javerzat, J. P. Fission yeast bub1 is a mitotic centromere protein essential for the spindle checkpoint and the preservation of correct ploidy through mitosis. J. Cell

Abstract. In cells containing disrupted spindles, the spindle assembly checkpoint arrests the cell cycle in metaphase. The budding uninhibited by benzimidazole (Bub) 1, mitotic arrest-deficient (Mad) 1, and Mad2 proteins promote this checkpoint through sustained inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during metaphase of mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes The mitotic spindle checkpoint. Gary J. Gorbsky. Biomedical Research Center, Room 266, 975 N.E. 10th St., University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, Oklahoma 73104, USA If the spindle checkpoint is defective (left pathway) then chromatid separation can occur before all the chromosomes are aligned at metaphase. The

Signaling dynamics in the spindle checkpoint response Biology Diagrams
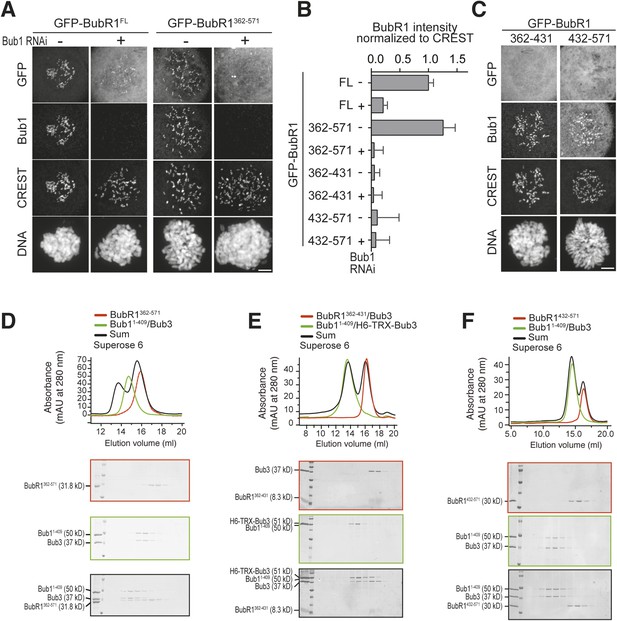
The spindle checkpoint inhibits these APC/C functions by inactivating Cdc20 through the Mitotic Checkpoint Complex (MCC), which consists of Cdc20 in complex with Mad2, BubR1 (Mad3 in yeast), and Bub3 30. The MCC inactivates the APC/C through a variety of mechanisms 31-35 and is the biochemical manifestation of the "wait anaphase" signal.

Abstract. The mitotic checkpoint is a specialized signal transduction pathway that contributes to the fidelity of chromosome segregation. The signaling of the checkpoint originates from defective kinetochore-microtubule interactions and leads to formation of the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), a highly potent inhibitor of the Anaphase Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C)—the E3 ubiquitin

The mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC): looking back and forth after 15 ... Biology Diagrams
Taylor, S. S. et al. Kinetochore localisation and phosphorylation of the mitotic checkpoint components Bub1 and BubR1 are differentially regulated by spindle events in human cells. J. Cell Sci